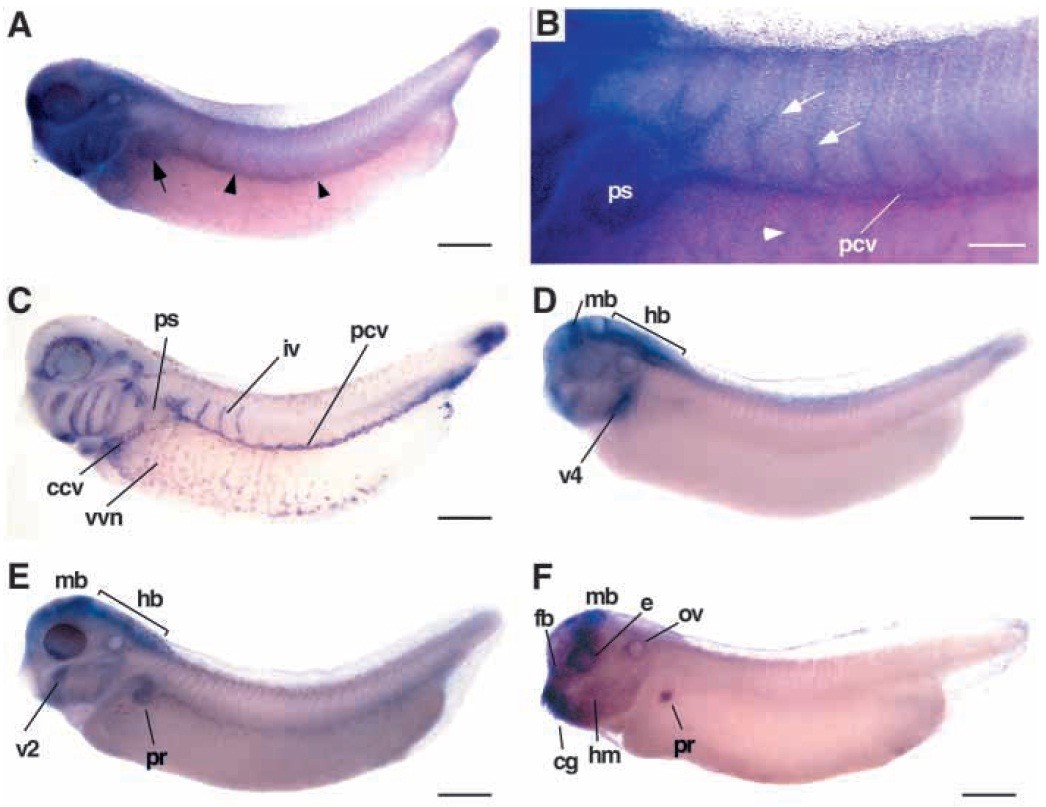
Fig. 1. Expression of Xenopus EphB4 in the embryonic vasculature. Transcripts for EphB4 (A,B), Msr (C), EphB1 (D), EphB2 (E), and EphB3 (F) were detected by whole-mount in situ hybridization of stage 34 (A,C-F) and 36 (B) embryos. Lateral views are shown with anterior to the left. (A) Expression of EphB4 in the pronephric sinus (arrow) and the posterior cardinal vein (arrowheads) of the embryonic trunk. (B) Close-up view of the trunk region to illustrate EphB4 expression in the intersomitic veins (arrows), the vascular vitelline vein network (arrowhead), the pronephric sinus (ps) and the posterior cardinal vein (pcv). (C) Staining with the vascular marker Msr visualizes the vascular vitelline network (vvn), the common cardinal vein (ccv), pronephric sinus (ps), the posterior cardinal vein (pcv), and the intersomitic veins (iv). (D-F) EphB1, EphB2 and EphB3 transcripts are prominently detected in the head (fb, forebrain; mb, midbrain; e, eye; ov, otic vesicle; hm, head mesenchyme), in specific visceral arches (v1, v4), the cement gland (cg), and the pronephric region (pr), but not in intersomitic veins. Scale bars: 500 mm (A,C-D); 200 mm (B).
Image published in: Helbling PM et al. (2000)
Copyright © 2000. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher and the copyright holder. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License.
| Gene | Synonyms | Species | Stage(s) | Tissue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| aplnr.L | agtrl1, angio1, apj, apjr, aplnr-a, aplnr-b, hg11, msr, Xangio1, X-msr, Xmsr | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 33 and 34 | blood vessel intersomitic vein posterior cardinal vein pronephric sinus vitelline vein aortic arch duct of Cuvier tail bud ophthalmic vein |
| ephb1.S | Elk-like kinase, LOC108717147, LOC108718198, Xek | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 33 and 34 | brain midbrain hindbrain |
| ephb2.L | cek5, LOC108697272, LOC108705066, LOC116410852, xEphB2 | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 33 and 34 | hyoid arch pronephric tubule brain midbrain hindbrain |
| ephb3.L | tck | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 33 and 34 | cement gland midbrain head mesenchyme pronephric kidney otic vesicle eye |
| ephb4.L | ephb4-a, ephb4-b, G51, htk, myk1, tyro11 | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 33 and 34 to NF stage 35 and 36 | intersomitic vein posterior cardinal vein pronephric sinus head vitelline vein intersomitic vessel |
Image source: Published
Permanent Image Page
Printer Friendly View
XB-IMG-131246