XB-IMG-146167
Xenbase Image ID: 146167
|
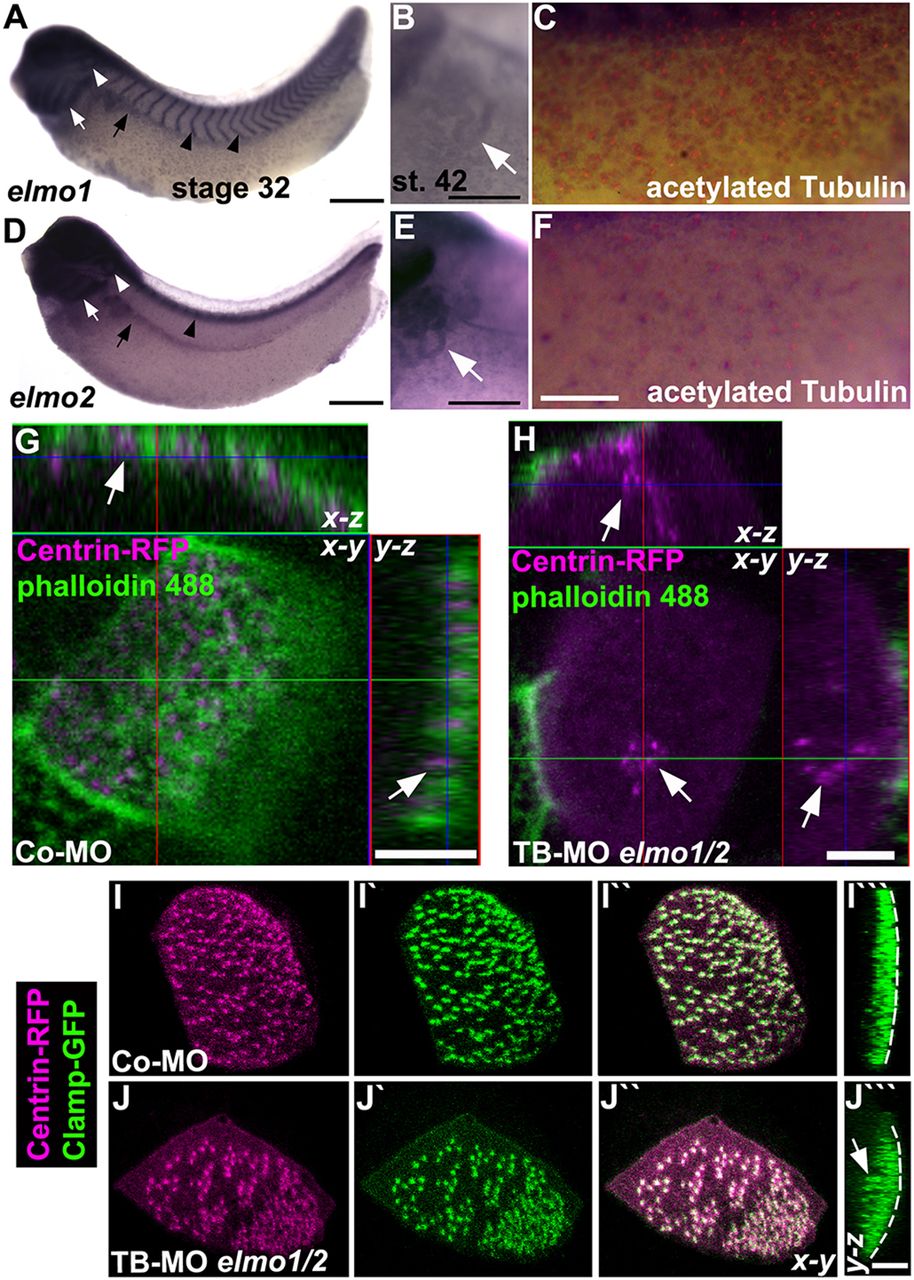
Fig. 2. ELMO1 and ELMO2 are expressed in ciliated organs and are required for ciliogenesis in Xenopus. (A-F) Expression of elmo1 (A-C) and elmo2 (D-F) in the head, branchial arches (white arrow in A,D), otic vesicle (white arrowhead), pronephric kidney (black arrow), throughout the epidermis at stage 32, and in the pronephric tubules (white arrow in B,E) at stage 42 of Xenopus development. In addition, elmo1 is expressed in the intersomitic vessels and elmo2 in the spinal cord at stage 32 (black arrowheads). Expression of elmo1 and elmo2 colocalised with acetylated Tubulin marking cilia at stage 32 (C,F; see also supplementary material Fig. S5C). (G,H) Xenopus embryos (stage 32) injected with TB-MO elmo1 and TB-MO elmo2 (each 4â
ng) and centrin-RFP mRNA colabelled with phalloidin 488 (for F-actin) revealed impaired migration and docking of basal bodies (arrows) to the apical membrane (H) as compared with embryos injected with Co-MO (8â
ng) (G). (I-Jâ´) Injection of Xenopus embryos (stage 32) with a lower dose of the TB-MOs (each 2â
ng) together with centrin-RFP and clamp-GFP mRNAs revealed partial basal body docking (arrows) and irregular basal body spacing (I-Jâ´) compared with proper apically docked and evenly distributed basal bodies in embryos injected with Co-MO (4â
ng) (I-Iâ´). Dashed line indicates the apical surface. Scale bars: 500â
μm in A,D; 250â
µm in B,E; 2â
mm in F; 5â
µm in G,H,Jâ´. Image published in: Epting D et al. (2015) Copyright © 2015. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher.
Image source: Published Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
